|
Thermistors
Objectives:
|
• Understand how a thermistor
works.
• Be able to describe the relationship between
resistance and temperature for a thermistor.
• Be able to describe applications of thermistors. |
 |
Task 1 - Starter
Remind the person next to you:
• What is meant by current
• The units of current
• The relationship between voltage and current for a
resistor.
• The relationship between voltage and current for a
bulb.
• The relationship between voltage and current for a
diode.
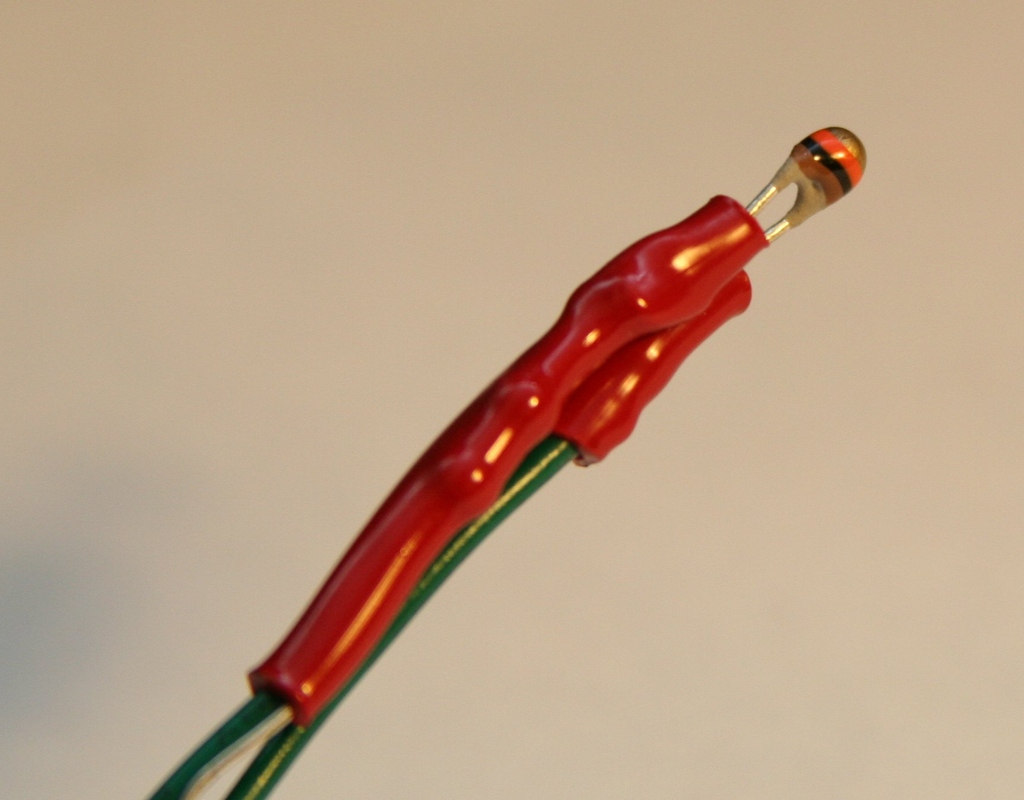
Task 2
| You are going to investigate how the
resistance of a thermistor changes with temperature. Your
teacher will give you a multimeter and a thermistor. You
will need to collect a beaker and some hot water. Test the
resistance of the thermistor at 10°C intervals, from 20°C to
90°C. You will need to draw a suitable table to collect
your results. |
 |
|
Temperature (°C) |
Resistance (kΩ) |
| 20 |
|
| 30 |
|
| 40 |
|
| 50 |
|
| 60 |
|
| 70 |
|
| 80 |
|
| 90 |
|
|
 |
Task 3
Plot a graph of your results.
• Temperature should be along the x-axis.
• Resistance should be along the y-axis.
• Both the axes should have labels and units.
• Give your graph a suitable title.
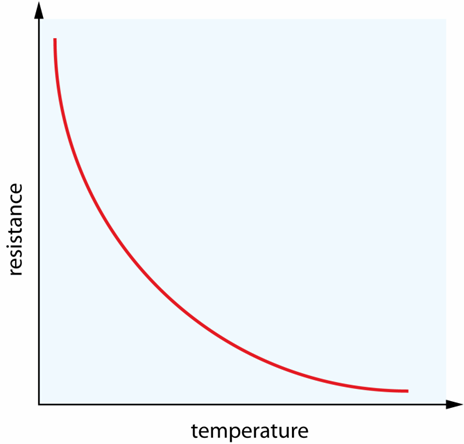
Your graph should look
something like this!
Task 4
Listen carefully as your teacher shows you
this presentation, and explains why a thermistor behaves like this.
Homework/Extension:
No homework this lesson.
|

