|
Evaporation
and Condensation I
Objectives
• Observe the cooling effects of evaporation.
• Know that evaporation occurs as a result of high
energy particles escaping from the liquid.
• Be able to describe and explain heating and cooling
processes involving evaporation and condensation in terms of the energy
of the particles involved.
Task 1 - Recap
Remind the person next to you:
- How the particles are arranged in a solid, in a liquid,
and in a gas.
- What we call a change of state from a solid to a
liquid, or a liquid to a solid.
- What we call a change of state from a liquid to a gas,
or a gas to a liquid.
Task 2
The particles in this liquid have energy.

As the particles vibrate there are many collisions
between them. This causes some particles to have more energy and other
particles to have less energy. We say there is a "varying distribution
of energies".
Think of the particles as being like bumper cars at
the fairground. Sometimes two or more bumper cars will collide and
stop altogether, and sometimes your bumper car is "bumped" from behind
and you end up travelling much faster than you were before!

Because of the collisions, and the resulting
"distribution of energies", some of the particles will gain enough energy to
escape from the top surface of the liquid. Your teacher will give you
some
notes and a copy of the diagram below:
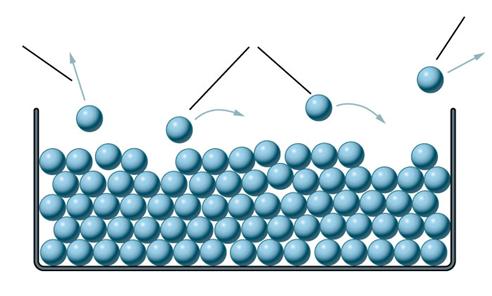
Stick the notes in your exercise book and write each of the following labels in the correct
place on the diagram:
some
particles escape from the liquid completely.
particles
with a high enough energy can escape from the surface of the liquid.
some
particles fall back into the liquid.
Task 3
Your teacher will provide you with a small beaker of
propanone. Use a pipette to drop a small amount onto the back of your
hand. Now blow on the propanone - you should notice a distinct cooling
effect!
|
Warning:
Propanone can be very damaging to eyes. You must wear
safety glasses at all times while carrying out this task. |
 |
Now complete the text on
your sheet to explain what you have just seen:
The _____________ depends on the __________ thermal energy of
the particles in the liquid. The particles with the most energy will
___________from the ______________ of the liquid. If the most
____________ particles escape the average energy of the particles
___________. This means that the fluid _________ as evaporation takes
place.
escape
cools energetic
temperature
decreases surface
average
Task 4
Condensation is the opposite of evaporation.
Particles in a vapour (gaseous) state lose energy and condense
back into a liquid state. This process of condensing usually happens
when the particles encounter a cool surface.
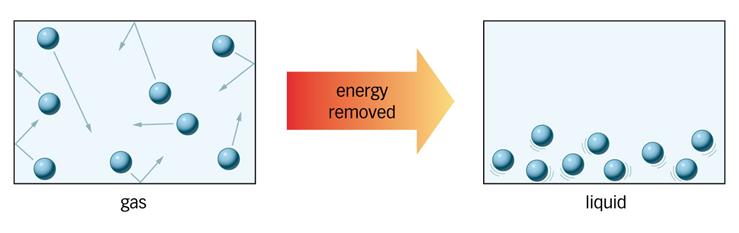
Your teacher will give you a copy of the
diagram
and notes above to stick into your exercise book.
Now explain, in as much detail as you can, why
condensation forms on the mirror, windows and walls when you run a hot bath.
You may want to use
this planning skeleton to help you.
Use as many of the following terms as you can in your
explanation:
evaporate evaporation
liquid
collision gain energy energetic
particles escape
vapour average thermal energy
temperature cool
lose energy
distribution
surface condense
condensation
|

