|
Specific Heat Capacity
Task 1 - Starter
Which do you think would keep you warmer on a cold
night...?
A - 1kg of water,
starting at 60°C...?
B - 1kg of aluminium,
starting at 60°C...?
C - Both the same...?
Your teacher will ask you to share your ideas with the
class, and then
Task 2
The Specific heat capacity
tells us
the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of a
substance by 1˚C. We will carry out a practical
task to find the specific heat capacity of water. We will use an electrical heater to raise the
temperature of 100g of water by 15˚C.
Discuss with the person next to you:
• How can
we work out the specific heat capacity from the quantities we measure?
(hint: look at the definition of
specific heat capacity!)
Task 2
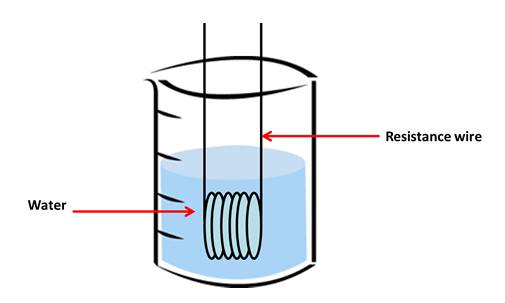
Collect the following apparatus:
• 250ml beaker
• a 100ml measuring cylinder
• a thermometer
• 12V power supply unit
• immersion heater coil
• an ammeter
• a voltmeter or multimeter
• 3 leads
Follow
these instructions to carry out the experiment and record all the
necessary measurements on
this sheet.
Task 3
Pack away your equipment carefully and complete the
calculations on your sheet to find the specific heat capacity of water.
The accepted value is 4200 J/Kg/°C.
How does this value compare with the value you
calculated? Discuss with your group any reasons you can think of
that your value might be too high or too low.
Write an evaluation explaining any reasons your value may
be too high or too low.
Task 4
The formula connecting energy, change in
temperature and specific heat capacity is shown below.
|
E
= m × c × ɵ
|
E =
Energy in Joules (J).
m = mass in
kilograms (kg).
c = specific heat
capacity,
in Joules per kg per °C (J / kg /
°C).
ɵ
= change in temperature in degrees Celsius (°C). |
Copy the formula into your
exercise book and try
these calculations. Higher tier students need to be able to
rearrange the formula.
Homework / Extension
Complete
these calculations.
Show full working for all problems.
|

