|
Newton's 2nd Law
Objectives
• Know that forces affect the motion of an object.
• Be able to compare the rates of acceleration of
objects, given information about the mass of the objects and the forces acting.
• Be able to use the equation F = m × a to solve
numerical problems involving force, mass and acceleration.
Task 1
Listen as your teacher
explains Newton's first two "Laws of Motion" and shows you a few
demonstrations.
Now watch
this video
clip which should also help to explain.
Task 2
Write the title "Newton's Laws of Motion" in your
exercise book, and copy the two laws given below:
Newton's First Law (basically) says:
|
if the forces on an object are
balanced (or zero)
the object will either
remain stationary or
continue moving at a constant
speed. |
Newton's Second Law (basically) says:
|
if the forces on an object are
unbalanced
the object will either accelerate
(speed up)
or slow down
and bigger
forces produce bigger accelerations |
Task 3
Stick
this sheet into your exercise book. Look at each of the
scenarios and use Newton's 2nd law to decide which object will
accelerate at the greatest / lowest rate.
Task 4
It is useful to express the second law as a formula.
Write the formula and equation triangle below in your exercise book.
|
F = m
× a
|
F = Force
m = mass
a =
acceleration |
And it can also be written as an equation triangle:
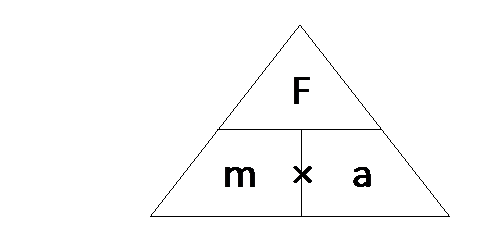
Note: the formula is given in the examination,
but the equation triangle is not given. If you find it
easier to use the equation triangle then it is up to you to remember it!
Task 5
Your teacher will go through two example calculations
with you. Pay attention and then copy the examples into your
exercise book, laying out the calculation methodically as your teacher
showed you.
Homework
Complete
this sheet of calculations. Show
full working for all calculations and remember to give units with your
answers.
|

