|
Convection
Objectives
• Carry out a practical task to investigate
convection.
• Describe the process of convection in terms of the
movement and changing density of regions of fluid undergoing heating or
cooling.
Task 1
We are going to investigate the cooling of water by
convection. We will monitor the temperature, both at the top and
the bottom of the beaker, every minute for 10 minutes.
Higher tier - we will also monitor a second beaker,
with a lid, to see the difference in the rate of cooling.
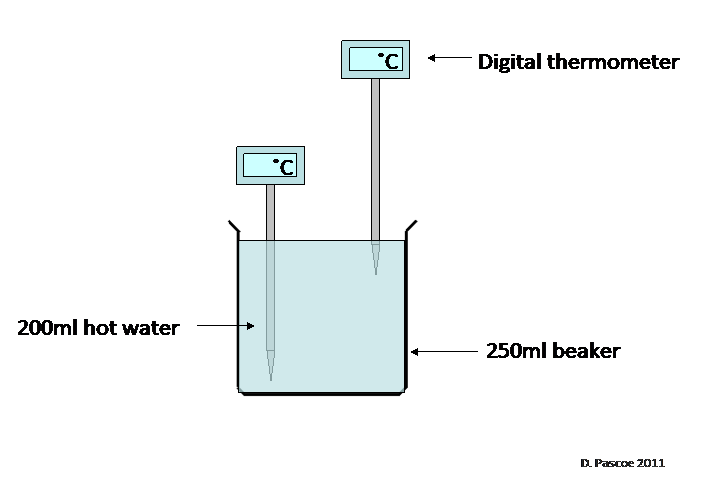
Your teacher will give you a
worksheet with a copy of the diagram and a table to record your
results.
Write the title “Investigating Convection” in your exercise book and
stick in the worksheet.
(Note - higher tier will need
this worksheet instead)
Task 2
We want to predict whether the water will be hotter at
the top or the bottom of the beaker. Write the subtitle
“Prediction” at the left hand side of the page and copy and complete
the sentence below:
"I think the water will be hotter at
the ______ of the beaker because..."
|
(Note to higher tier groups: forget about the second
beaker for now - you only need to worry about the open beaker! )
Try to give a reason, using technical scientific
language, to explain your prediction.
Task 3
Carry out the experiment according to the instructions on
the worksheet. Record your results in the table provided.
Task 4
Your teacher will give you a
copy of the text below. Fill in the gaps with the words
provided.
(Higher tier will need
this sheet instead)
Convection is taking place in the water. The water at the
top of the beaker cools __________ rapidly than the water at the
______________, because it is in contact with the air which is
at a lower temperature. These cooler regions of fluid
_______________ so their density ________________ and they sink.
Regions of warmer fluid, which are _________ dense, rise up to
replace them. This means the water is warmest at the _________
of the beaker, and coolest at the _____________ of the beaker.
Convection is
also taking place in the air above the water. The air at the
__________________ of the water is warmed and so ______________
and decreases in density. It rises, carrying _________ energy
away with it. _________ air sinks to replace it. If we add a
lid, it stops the convection current in the air by preventing
the warm air escaping, which slows down the rate of cooling.
|
Extension / MAT task
Plot a graph of the results for the open beaker.
The points should form a smooth curve. Calculate the gradient of
the curve at 1 minute and at 9 minutes.
· What does this gradient
represent? What are the units?
· which of the two gradients is
larger? Can you explain why?
|

