|
Energy Transfers I
Task 1 - Starter
Look at
this presentation and answer the questions to see how much you
understand about heat transfer.
Task 2
This hot drink contains energy. The hot drink
will cool down because it is transferring energy to its surroundings.
Energy will be transferred until it reaches the same temperature as its
surroundings.

Now look at this cold drink. Is energy being
transferred here? Discuss with the person next to you what you
think is happening.

Your teacher will ask some of you to share your ideas
with the class.
Now stick
this sheet of notes in your exercise book and explain what you think
will happen in the space provided.
Task 3
Lots of factors affect the rate at which energy is
transferred. Look at
this presentation which explains some of the factors which can
affect the rate of cooling.
• The temperature difference between the object
and its surroundings.
• The size and shape of the object, and especially
the surface area.
• The type of material the object is made of.
• What the object is in contact with.
Task 4
Complete
these tasks and questions. Answer all questions in full
sentences.
1.) Write a list to summarise all the things that can
change the rate at which heat energy is transferred.
2.) Explain how you could reduce the rate of heat
energy transfer from a hot drink.
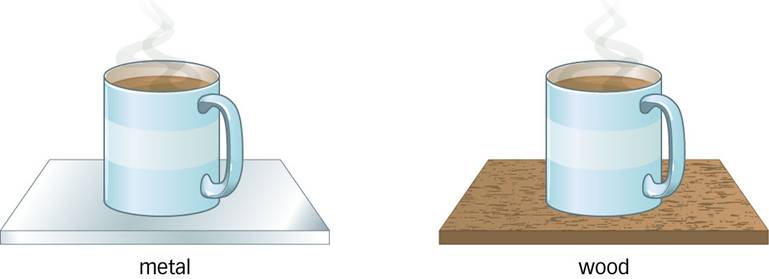
3.) Which cup of coffee will cool down faster?
Explain your answer.
4.) What can you say about the rate of heat energy
transfer in an object that is at the same temperature as its
surroundings?
Task 5 - Extension
Watch
this video clip which explains how a vacuum flask keeps a drink
warm.

Stick in
this diagram of a vacuum flask and try these questions from the AQA
textbook:
1.) Describe in detail how a vacuum flask keeps a drink
warm. You may wish to use the following terms in your
explanation:
conduct
convection thermal energy
transfer vacuum
radiation plastic
insulator surface
shiny matt/dull
light dark
escape evaporation
contained free
electrons
2.) What kind of material would you put at the top of
the vacuum flask (i.e. for the stopper)
3.) Why should you fill up a vacuum flask rather than
half-fill it? (higher tier)
|

