|
Motion Graphs - Part
III
Objectives
• Be able to sketch or plot speed-time graphs for
objects moving at constant speed and constant acceleration.
• Be able to interpret a speed-time graph in order to
describe the motion of the object shown.
• Be able to calculate acceleration and distance
travelled from a speed/time graph.
Task 1 - Recap
The motion graphs we have looked at so far have all be
distance-time graphs. Your teacher will give you a
copy of the graph and questions below. Stick the graph into
your exercise book and answer the questions.
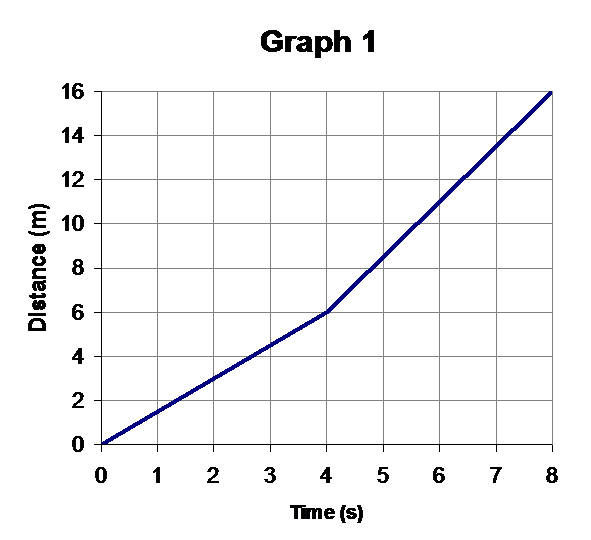
(a) Describe the motion in words.
(b) Calculate the speed in the first 4 seconds.
(c) Calculate the speed in the next 4 seconds.
(d) Calculate the average speed.
Task 2
|
We now need to look at a second type
of motion graph - a speed-time graph.
Look at
this presentation to see how
speed-time graphs are plotted and how we
can interpret the information on the graph. |
 |
Task 3
|
You will need to practise drawing distance time
graphs. Read the information below and plot a speed-time graph of the data given.
Your teacher will give you a
copy of the
information to stick in your exercise book. |
 |
|
A cyclist sets off
and accelerates from rest to a speed of 12m/s, taking 6
seconds to reach this speed. He maintains this speed
for 30 seconds. The cyclist then accelerates again, taking 8
seconds to reach a speed of 16m/s. He maintains this speed
for a further 20seconds, then decelerates to a stop, taking
10 seconds to come to rest.
|
Teacher note: here is a
completed version of the graph in excel format.
Task 4
We need to learn two rules, which will allow us to
find out the distance travelled by an object and the rate of
acceleration for objects which are not travelling at a constant speed.
|
The gradient of a speed-time graph is the
acceleration.
|
and
|
The area under a speed-time graph is the
distance travelled.
|
Learn both of these
- they
are not given!
Now, use the rules you have learned to answer these
questions. Copy each question into your book and show full working
for your calculations.
1) What is the
speed of the cyclist after:
a) 2 seconds? b) 10
seconds? c) 40 seconds?
d) 70 seconds?
2) What is the acceleration of the cyclist between
2
and 4 seconds?
3) What is the
acceleration of the cyclist between 20
and 30 seconds?
4) What is the acceleration of the cyclist between 40
and 44 seconds?
5) What is the
acceleration of the cyclist between 64 and 70 seconds?
6) What is the distance travelled by the
cyclist in the first 6 seconds?
7) What is the total distance travelled by the
cyclist?
Homework
Complete
this worksheet.
|

